Decision Tree(결정 트리)
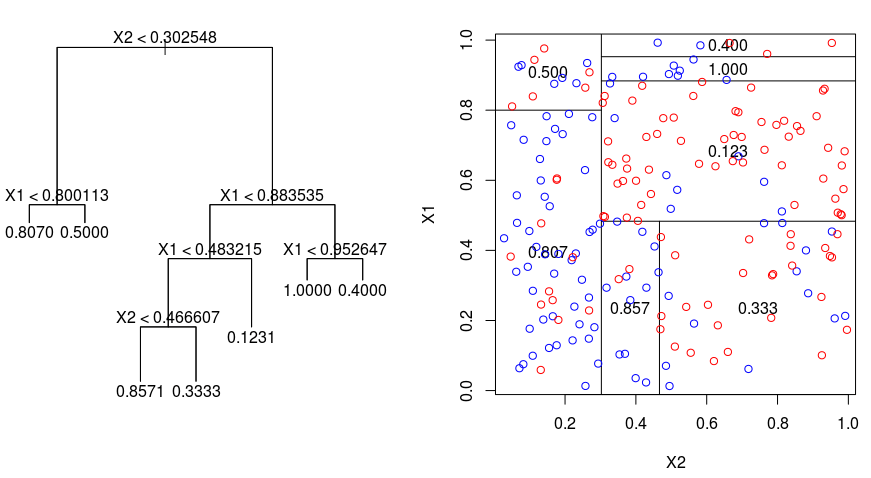

데이터를 통해 Branch를 구성하고 이를 통해 분류, 회귀까지 할 수 있는 모델이다.
이 중 분류 모델의 경우 Impurity가 최소가 되는 방향으로 Branch가 생성되며, 여러 Branch로 구성된 최종 형태가 거꾸로 세운 나무 같아 트리 모델이라고 부른다. Impuriy는 Entropy와 Gini index로 측정된다.
Impurity 측정 지표
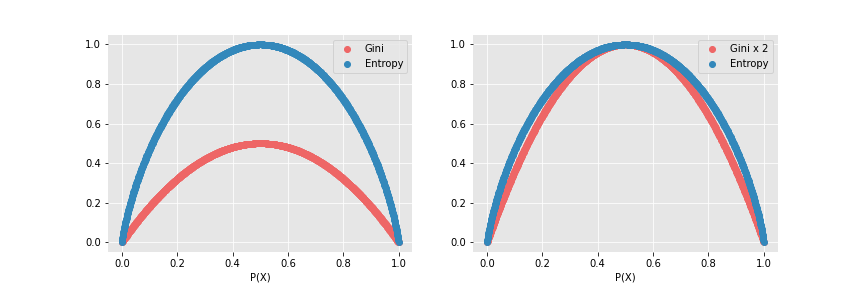
Impurity라는 이름처럼 Entropy, Gini index 모두 고유한 성분만 있을 때 최솟값을 가지고, 반반 섞여 있을 경우 최댓값을 가진다. 두 지표 중 Entropy는 $log$ 항이 있어, 상대적으로 계산에 더 오랜 시간이 걸린다.
Entropy
$$ E = -\sum_{k=1}^K p(y_k) \log_2 p(y_k) $$
- 최솟값 : 0. 최댓값 : 1
Gini index
$$ \text{Gini} = 1 - \sum_i p(i|t)^2 $$
- 최솟값 : 0, 최댓값 : 0.5
Branch 구성하기 : Information Gain(Ratio)
Branch는 매번 Impurity가 최소가 되도록 생성된다. 가능한 분기 중 최적의 경우를 찾기 위해 Entropy를 활용하는
Information Gain(ID3) 및 Information Gain Ratio(C4.5) 방법이 있다. 또한 Gini index를 기반으로하는 CART(Classification and Regression Tree)가 있다.
Information Gain
$$
I G=H-\left(\sum \frac{\left|D_j\right|}{|D|} * H_j\right)
$$
Information Gain은 Branch 생성 전-후의 Impurity 차이를 통해 계산한다.
매 시행마다 Gain이 가장 큰 특성에 대해 Branch가 생성되는 것이다. 굉장히 직관적이다.
하지만 경우의 수가 많은 특성만 선택될 가능성이 높다는 문제점이 있다. 이 경우 Entropy 자체는 낮출 수 있어도, 그 Branch가 의미 있다고 보기 힘들다. 또한 Branch 개수가 많아져 과적합이 발생한다.

Information Gain Ratio
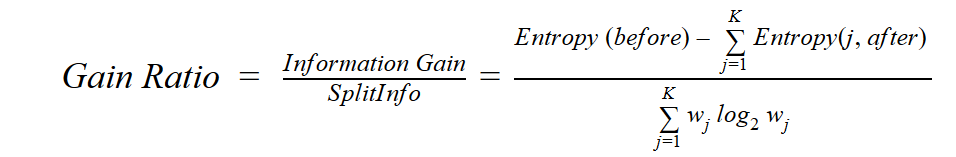
Branch로 선택 시, 경우의 수가 많은 특성에 쏠리는 Information Gain(IG)의 단점을 보완했다.
단순히 Branch 생성 전-후의 Entropy만 비교한 IG와 달리, IG Raio에선 IG를 Split(Intrinsic) Information로 정규화하여 Branch 생성으로 인한 데이터 자체의 Entropy까지 고려한다.
이를 통해 경우의 수가 많은 특성에 쏠리는 문제를 해결했다.
CART
Information Gain(IG)와 동일하게 전-후 Impurity 차이를 통해 Branch를 선택한다. 다른 점은 Impurity 측정을 Gini index로 하고, 매 시행 마다 2 개의 Branch로만 분기된다는 점이다. 연속형 변수를 직접적으로 사용할 수 있다는 점도 CART의 특징이다.
각 알고리즘(ID3(IG), C4.5(IG Ratio), CART)의 특성을 비교하면 아래와 같다.
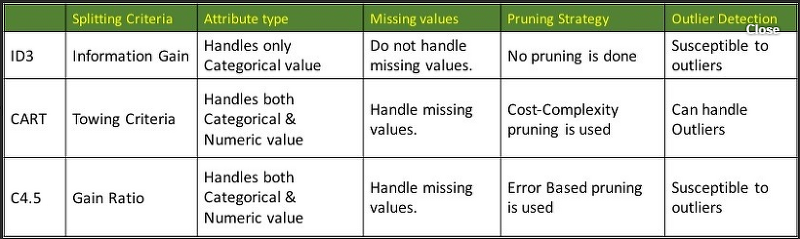
참고
Decision Tree의 Impurity 지표 (Entropy, GINI index, GR)
* 이번 포스팅은 Decision Tree에 대한 기본적인 이해가 있다는 것을 가정한다. Decision Tree는 데이터를 이용하여 tree 구조를 만드는 것을 통해 이를 분류하거나 결과값을 예측하는 분석 방법을 말한
process-mining.tistory.com
Information Gain, Gain Ratio and Gini Index
Information Gain, Gain Ratio and Gini Index are the three fundamental criteria to measure the quality of a split in Decision Tree.
tungmphung.com
Decision Trees: Gini vs Entropy ⋆ Quantdare
What is the difference between gini or entropy criteria when using decision trees? In this post, both of them are compared.
quantdare.com
Information gain ratio - Wikipedia
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia In decision tree learning, Information gain ratio is a ratio of information gain to the intrinsic information. It was proposed by Ross Quinlan,[1] to reduce a bias towards multi-valued attributes by taking the number a
en.wikipedia.org
